Strip foundation
Contents |
[edit] What are foundations?
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
Very broadly, foundations can be categorised as shallow foundations or deep foundations. Shallow foundations are typically used where the loads imposed by a structure are low relative to the bearing capacity of the surface soils. Deep foundations are necessary where the bearing capacity of the surface soils is not adequate to support the loads imposed by a structure and so they need to be transferred to deeper layers with higher bearing capacity.
[edit] What are strip foundations?
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation that are used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support for linear structures such as walls or closely-spaced rows of columns that are built on top of the foundation, placed centrally along their length.
[edit] When are strip foundations suitable?
Strip foundations are suitable for supporting linear loads in most types of subsoil, but they are most suitable where soil is of relatively good bearing capacity. They are particularly suited to light structural loadings such as those found in many low-rise or medium-rise domestic buildings - where mass concrete strip foundations can be used. In other situations, reinforced concrete may be required. Older buildings may variations on strip foundations such as brick strip foundations.
[edit] What size and shape should strip foundations be?
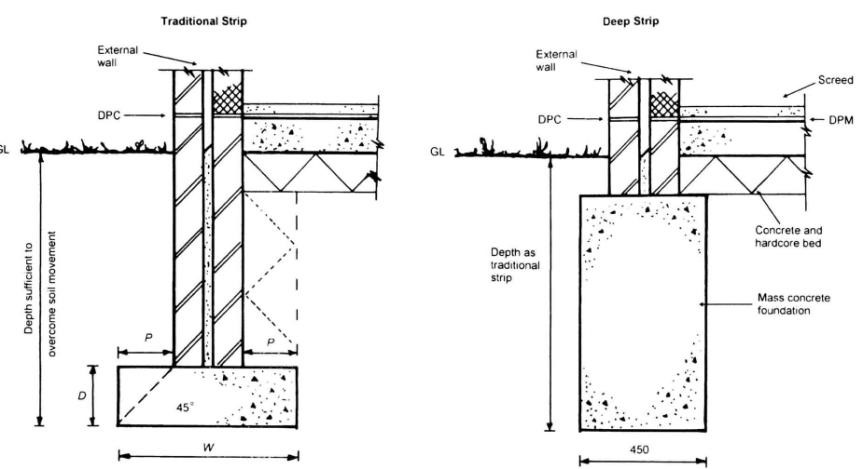
The size and position of strip foundations is typically related to the overall width of the wall they are supporting. The depth of a traditional strip foundation is generally equal to or greater than the overall wall width, and the foundation width is generally three times the width of the supported wall. This results in the load being spread at 45º from the wall base to the soil.
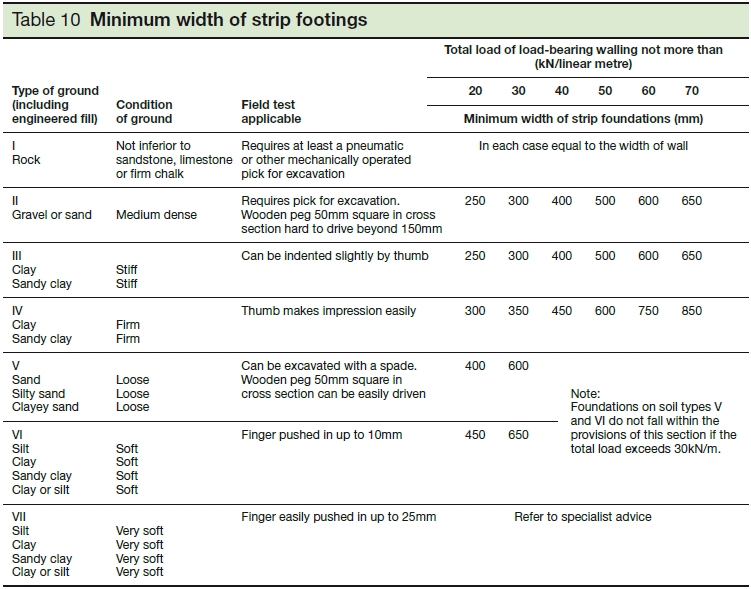
Approved document A of Building Regulations defines minimum widths for strip footings based on the type of ground and load-bearing wall, although it is generally advisable to consult a structural engineer when designing foundations.
The underside of strip foundations should be deep enough to avoid frost action; for example, at least 450 mm unless they are bearing on rock, and at least 1 m on high shrinkage clays.
Deep strip foundations may be necessary where soil with a suitable bearing capacity is deeper.
Wide strip foundations may be required where the soil is soft or of a low bearing capacity, so as to spread the load over a larger area. Wide strip foundations will typically require reinforcement.
[edit] What sort of foundations might be used if strip foundations are not suitable?
Where there are higher localised loads, such as columns, pad foundations may be used. See pad foundations for more information.
Where ground conditions are poor, settlement is likely, or where it may be impractical to create individual strip or pad foundations for a large number of individual loads, raft foundations may be used. See Raft foundations for more information.
Where the bearing capacity of the surface soils is not adequate to support the loads imposed by the structure, deep foundations such as pile foundations may be used. See Pile foundations for more information.
Larger or more complex buildings may involve the use of a number of different types of foundation.
Additional guidance is available in BRE's Simple foundations for low-rise housing: 'rule of thumb' design.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Approved Document A.
- Bearing capacity.
- Brick strip foundation.
- Building foundations.
- Driven piles.
- Footings in foundations.
- How deep should foundations be.
- How to design a pad foundation.
- Pad foundation.
- Pile foundations.
- Raft foundation.
- Rubble trench foundation.
- Stepped foundation.
- Subsoil.
- Trench fill foundation.
- Types of excavation.
- Types of pad foundation.
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.




























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.
Very informative post...good information provided.
Thank you. Ed